Artificial Intelligence is a broad term, so it can quickly get confusing. One person says that AI means chat tools. Someone else means automation. Someone else means predictions on the dashboard. They’re all talking about real things, but they’re not always talking about the same thing.
Stanford AI Index 2025 Reports indicate that 78% of organizations used AI in 2024 (up from 55% in 2023). It also notes that the rate of use of AI in at least one business function has risen to 71% (up 33% in 2023).
This is why it is important to understand the types of artificial intelligence in a practical way. Once you know the key groups, you can choose the right approach, set the right expectations, and avoid building the wrong tool for the task.
This article uses a simple “what you can do with it” view, because it is the easiest to apply in real projects.
The 5 most famous types of artificial intelligence used today
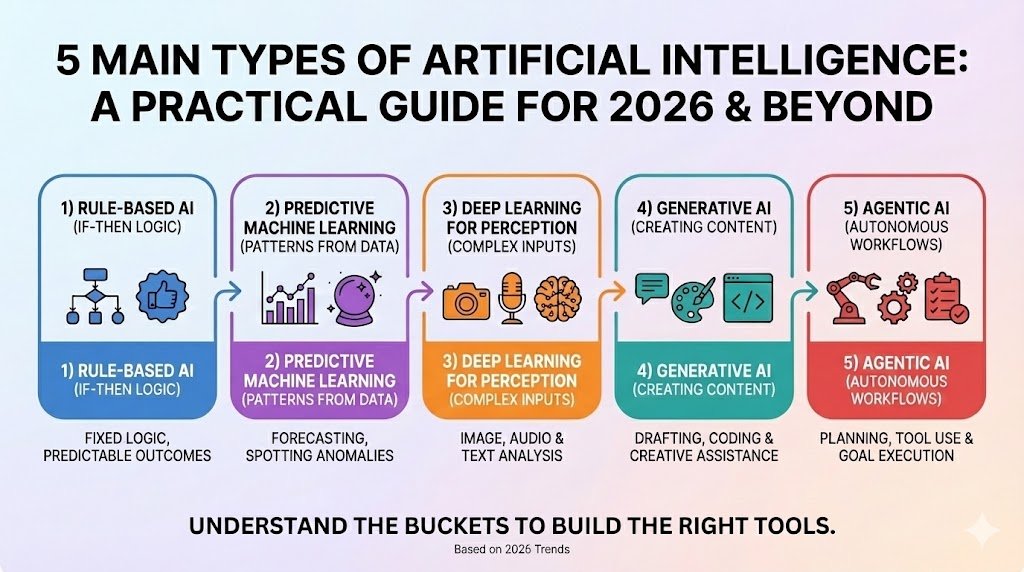
Here are the five main types of AI that appear in everyday business tools and software products. They often work together, but each type has a different strength.
1) Rule-based artificial intelligence
Rule-based AI is the simplest type. It follows the established logic written by people. Think of it like, “If this happens, do that.” : If your team keeps mixing up terms like rules and models, that’s… Artificial Intelligence Dictionary Helps maintain language consistency.
One common type of AI in legacy enterprise systems is a rules engine that routes tickets, flags policy issues, or approves simple cases.
Where it works best
It works best when:
- The rules are clear and stable
- You need predictable results
Example in simple words
A support workflow can automatically flag a ticket when it contains certain words, then assign it to the correct queue. Learning doesn’t happen here. It’s still very useful because it’s fast and consistent.
Limits of knowledge
If the rules change too often, maintenance becomes painful. If real life has too many contingencies, the rules can become a tangled mess.
2) Predictive machine learning
Predictive machine learning learns patterns using historical data. Instead of fixed rules, it uses examples and results to predict.
This is what a lot of people mean when they say “artificial intelligence” in analytics. It answers questions like “What’s likely next?”
If you want a clear comparison of prediction versus generation, read on Generative AI vs Predictive AI.
Where it works best
Works well for:
- Demand forecasting and lead recording
- Detect anomalies in transactions and records
Example in simple words
The e-commerce team can predict which orders are most at risk of returns using past order behavior and product attributes. The team can then adjust communications and policies before a return occurs.
Limits of knowledge
Predictive models depend on the quality of the data. If the labels are weak, the model will learn the weak signals. If the data changes, accuracy can quietly decline.
3) Deep learning for perception
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that is powerful in perception tasks. It is commonly used for image, audio, text classification and style-heavy input.
If you turn perception into real advantage, Artificial intelligence in web applications Shows how teams ship it into products.
Deep learning is powerful, but it also needs more data, more computation, and careful evaluation.
Where it works best
Fits well for:
- Support medical imaging and quality checks
- Speech-to-text conversion and visual inspection
Example in simple words
The manufacturing team can use camera feeds to detect visible defects. A deep learning model can detect patterns that humans might miss during long shifts, then route only suspicious cases to a human reviewer.
Limits of knowledge
Deep learning can be difficult to explain in simple terms. This is good in some use cases, but risky in high-stakes decisions unless you add verifications, monitoring, and audit trails.
4) Generative artificial intelligence
Generative AI creates new content rather than just predicting ratings or scores. This includes creating text, creating images, and creating code. This explanation is on How does generative artificial intelligence work? Makes boundaries and review steps easier to explain to teams.
This is the category that makes AI feel “human” to many people, because it can write, summarize, and chat in a natural way.
Where it works best
It is useful for:
- Crafting content and support responses
- Help teams write code and documentation faster
Clear example
The product team can use the chat interface to turn internal feedback into an easy-to-use draft Help article. A developer can use the Coding Assistant to create the first version of the function, then review it and add tests.
Microsoft Research conducted a controlled study and found that developers using GitHub Copilot completed the programming task 55.8% faster From the control group.
What “types” exist within generative AI?
People often ask about types of generative AI because this bucket is broad. In practice, teams use text and image generative tools. They also use it for symbol and sound, depending on the product.
Limits of knowledge
Generative tools can appear confident while being wrong. This means a matter of review and verification. If the content impacts users or compliance, you need a clear consent step.
5) AI agent
Agent AI is the “doing tasks” layer. He can plan steps, use tools, and continue working until he reaches a goal or stopping rule. It’s not just a chat response. It’s a ring.
This is a big shift because it can move work forward within systems, not just suggest what a person should do.
Where it works best
It can help with:
- Convert tickets into secure first drafts
- Run repeatable workflows such as test runs and code inspection
Example in simple words
An engineering team can set up an agent that reads the bug report, tries to reproduce it, runs tests, and then proposes a patch in a pull request. People are still reviewing and integrating, but the repetitive steps are getting smaller.
Limits of knowledge
Access to the tool needs guardrails. If the agent is able to write to production systems, errors can scale. The best setup uses limited permissions, full logs, and approval portals.
Gartner predicts More than 40% of AI projects will be canceled by the end of 2027, due to costs, unclear value, or weak risk controls.
How these products and workflows become real
In real software, these elements are not kept in isolation. Most teams build a mix of capabilities, and that mix becomes one of several types of AI systems.
Here’s what it looks like in practice:
- The rules engine handles base routing, and the predictive model handles risk scoring.
- Deep learning model flags issues in images, confirms one reviewer.
- The generative layer shapes the content, and the agent layer turns it into tasks within your tools.
This is why planning is important. You don’t choose “artificial intelligence.” You choose which parts should be there and how they connect to users and processes.
That’s where WebOsmotic fits in
WebOsmotic Helps teams turn AI ideas into practical product features with clear scope, measurable outcomes, and secure rollouts. This includes choosing the right form type, building a workflow around it, and setting up guardrails such as registration and review portals.
If you’re planning a new build or upgrade of an existing platform, the quickest win is usually clarity: what the tool should do, how it will measure, and how it will remain secure at scale.
Frequently asked questions
1) What are the main types of AI used in products today?
Most products use a combination of rule-based reasoning, predictive machine learning, deep learning, generative AI, and agentic AI. The right mix depends on the job, inputs and level of risk.
2) Is machine learning always better than rule-based AI?
Not always. Rule-based systems are great when the logic is stable and the results must be predictable. Machine learning helps most when patterns are complex and data can support the learning.
3) Where does generative AI fit into business software?
Best suited for drafting and assistance tasks, such as writing responses, summarizing internal notes, and speeding up the programming process. It still needs to be revised when accuracy is important.
4) What makes agentic AI different?
Agentic AI can plan steps and use tools to complete tasks in a loop. It goes beyond simply responding to prompts and can proceed with work within a controlled workflow.
5) How do teams choose the right approach to AI?
Start with the exact outputs you need, then validate your inputs and define success metrics. Choose the simplest approach that achieves the goal, then add safety steps based on the risks.